Hashes: An Introduction & Why They Are Foundational To The Internet & Blockchains
"The phrase 'one-way hash function' might sound arcane and geeky, but hash functions are the workhorses of modern cryptography."
— Bruce Schneier
Hash Functions
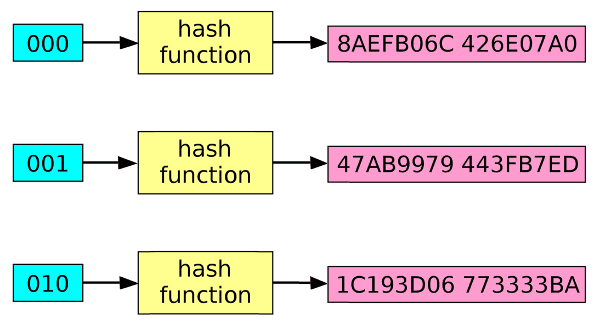
Hash functions are functions with outputs all the same size. These outputs are referred to as hashes. For example, all Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA1) hashes have 20 bytes. Hash functions can efficiently confirm the integrity of files. For example, to confirm two terrabyte sized files are identical, it is easier to compare two hashes than all the bits!
One Way Functions

Cryptography requires hash functions that are one way functions. One way functions are functions that are hard to invert. For example, computers can quickly find products of large primes, but, they cannot quickly factor the results.
Collision Resistance

Cryptography also requires hash functions that are collision resistant. Collision resistance is a property of hash functions whereby it is difficult to find objects with the same hash. MD5 is a hash function discovered to have weak collision resistance. One could in principle maliciously modify information such that MD5 hashes would not detect the change. For a sobering example, consider Alice replacing this letter of recommendation, to the administrator of Gaul, with this alternate letter. The MD5 hash of both Postscript files is 0xa25f7f0b29ee0b3968c860738533a4b9!
Collision resistant hash functions make password based authentication systems more secure since only password hashes are stored. Authentication is performed by comparing hashes. Even if all password hashes are made public, it is still not possible to easily determine the passwords! (A attacker can eventually determine the passwords. Therefore, many systems require passwords to be changed every few months.)
Blockchains

Blockchain systems continually use hashes to confirm the integrity of much information. Hashes also provide short unique identifiers for accounts, keys, transactions, blocks and state.
Conclusion

Hashes are vital for the Internet, blockchains and beyond. They are truly the workhorses of cryptography.
Feedback
You can contact me by clicking any of these icons:
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank IOHK (Input Output Hong Kong) for funding this effort.
License
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



